The National Institutes of Health today announced a new initiative aimed at accelerating the innovation, development and commercialization of COVID-19 testing technologies, a critical component needed to return to normal during this unprecedented global pandemic. With an investment of $1.5 billion in federal stimulus funds, the recently launched Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics (RADx) initiative will inject funds into early innovative technologies to accelerate the development of rapid and widely accessible COVID-19 tests. At the same time, NIH will seek opportunities to rapidly advance more advanced diagnostic technologies through the development process toward commercialization and broad availability. NIH will work closely with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority (BARDA) to advance these goals.
The stimulus investment leverages NIH’s robust research efforts already underway focused on the prevention and treatment of COVID-19, including the recently announced plan. Accelerate therapeutic interventions and vaccines against COVID-19 Public-private partnership to coordinate the international research response to the pandemic.
“We need all innovators, from the basement to the boardroom, to come together to advance diagnostic technologies, no matter where they are in development,” said NIH Director Francis S. Collins, MD, Ph.D. “Now is the time for that unrivaled American ingenuity to bring the best and most innovative technologies to make COVID-19 testing widely available.”
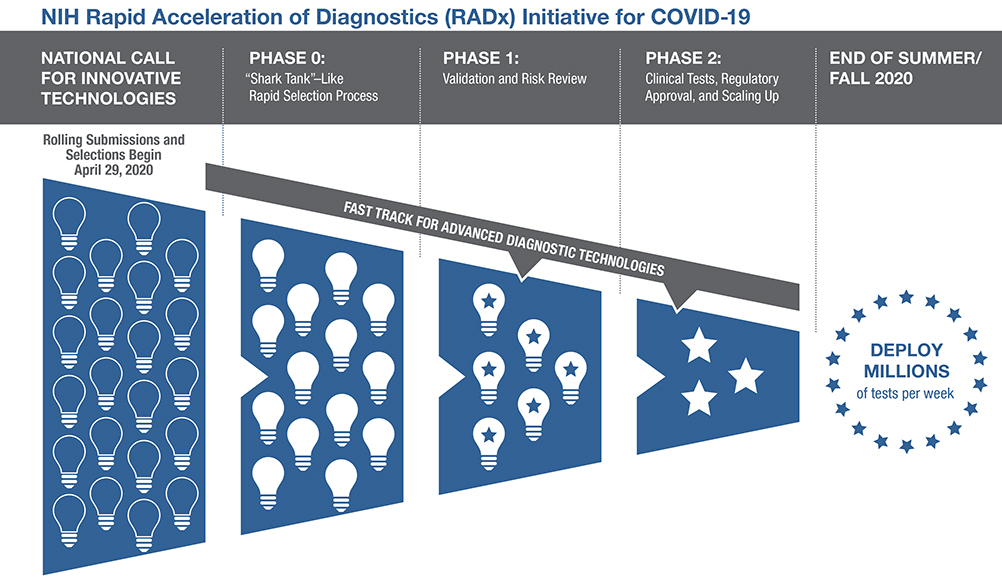
As part of this initiative, NIH is urging all scientists and inventors with rapid testing technology to compete in a national COVID-19 testing challenge for a share of up to $500 million across all phases of development. The technologies will undergo a rapid and highly competitive three-phase selection process to identify the best candidates for at-home or point-of-care COVID-19 testing. Finalists will be paired with technical, business and manufacturing experts to increase the odds of success. If certain selected technologies are already relatively advanced in their development, they can be placed on a separate track and immediately advanced to the appropriate step in the commercialization process. The goal is to make millions of accurate, easy-to-use weekly tests available to all Americans by the end of summer 2020, and even more in time for flu season.
“Americans are innovators and creators,” said Bruce J. Tromberg, Ph.D., director of the NIH’s National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB). “We need America’s tech experts, innovators and entrepreneurs to step up on one of the toughest challenges we’ve faced as a country, to help us safely return to public spaces.”
While diagnostic testing has long been a mainstay of public health, newer technologies offer patient-friendly and user-friendly designs, mobile device integration, reduced costs, and greater accessibility both at home and at the point of care. RADx will expand the Point of Care Technology Research Network (POCTRN) established several years ago by NIBIB. The network will use a rapid and flexible process to inject financing and improve technological designs at key stages of development, with expertise from technological innovators, entrepreneurs and business leaders from across the country. POCTRN supports hundreds of researchers from multiple universities and companies through five technology centers:
- Emory University/Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta
- Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore
- Northwestern University, Evanston, Illinois
- University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester/University of Massachusetts Lowell
- Consortia to Improve Medicine with Innovation and Technology (CIMIT) at Harvard Medical School/Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston
Led by the CIMIT Coordinating Center, the network has brought together expert review boards covering scientific, clinical, regulatory and commercial domains that will rapidly evaluate technology proposals. To implement new products starting in late summer/fall 2020, a rapid and parallel process will allow for rapid turnaround of projects. Projects will be evaluated at each milestone and must demonstrate significant progress to receive continued support.
About the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB): NIBIB’s mission is to improve health by leading the development and accelerating the application of biomedical technologies. The Institute is committed to integrating engineering and physical sciences with biology and medicine to advance our understanding of diseases and their prevention, detection, diagnosis and treatment. NIBIB supports research and development of emerging technologies within its internal laboratories and through grants, collaborations and training. More information is available on the NIBIB website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation’s medical research agency, includes 27 institutes and centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency that conducts and supports basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures of common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit www.nih.gov.
NIH…Turning discovery into health®
###


